




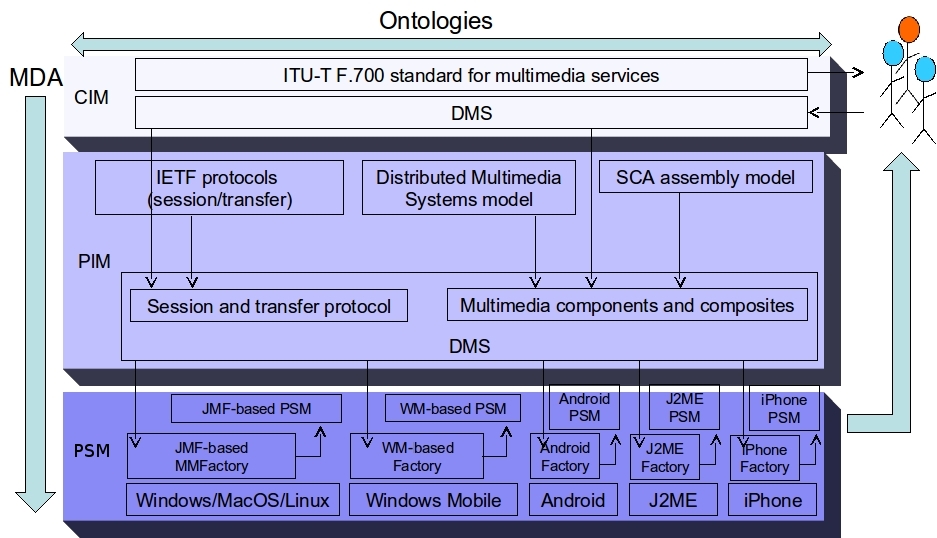
In order to facilitate the interoperability and the integration of different systems, we studied novel approach to adapt the model-driven engineering. In order to do that, we studied a novel architecture increasing the semantic of the different layers Computation Independent Model (CIM), Platform Independent Model (PIM), Platform Specific Model (PSM) (cf. OMG) and the associated transformations (i.e. mappings) thanks to ontological modelling. We applied this approach for a multimedia ontology-driven architecture.
During the last years, the number of ontologies has grown enormously. Several ontologies concern the same domains (medicine, biology, etc.). It seems interesting to be able to automatically combine these very dynamic information for an efficient exploration and retrieval process. We need to provide novel mechanisms or tools in order to connect the different ontologies about a specific domain for collaboration and/or cooperation and exploration purposes. To do this, we studied novel technics for efficiently aligning the data (concepts and DL formulae) and computing distributed reasoning. The architecture allows reasoners to check the consistency of each ontology locally and the networked ontologies (set of ontologies + alignments) globally.

Considering the enormous amount of model representations about various domains, there is an emerging need for representing these models in navigable graphs that can help analyse and explore the semantic expressed by them. Moreover, considering different graphs to be matched for increasing the knowledge about a domain, it is also important to map the graph's concepts in order to facilitate the interoperability between the considered graphs preserving as much as possible the relevant information and reducing the overall redundancy. In order to do that, we developed novel graph manipulation methods and new alignment approaches to formalize the concept expressed by the models by minimizing the loss of information and the time requested by this process.
